Developer agility is key to increasing the efficiency of software development. One of the primary areas in which development could be slowed down is the process that kicks in once the code is merged by the developers. In a typical organization with DevOps practices in place, CI/CD is set up for the application development, where developers are involved in the process until the code is merged.

Then, CI pipelines take over the process of doing E to E testing and provide feedback to the developers. With applications moving towards being more cloud native, the number of components that run in containers has become increasingly high. Because these components are also of a cloud native nature, their delivery becomes agile and the software updates to these components become more frequent. Realistically, it should be easy enough to test the changes in these components in the pipelines.
This leads to an important question:
- How do we build a CI pipeline where verification and hardening of the infrastructure components can be done easily and devote more time to developing the pipeline jobs related to the application business logic?
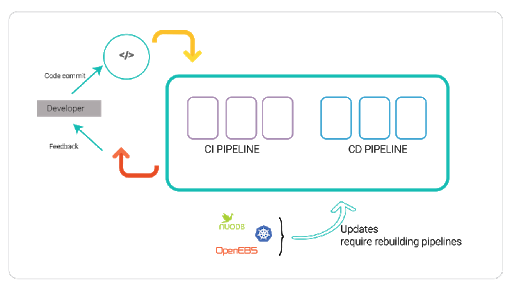
The answer to this question lies in adopting the cloud native chaos engineering into the CI/CD pipelines. Chaos Engineering is quickly becoming the most sought after method wheb building resiliency into cloud native applications. In ideal chaos engineering applications, chaos should be inserted at all layers (application, database, networking, storage, and Kubernetes), both in the CI pipelines and in production. Litmus is a chaos engineering framework designed to help with this specific need. For a good introduction to Litmus, see the Litmus docs (https://litmusdocs.openebs.io/ )
In this post, we specifically want to focus on what Litmus deployers and chaos jobs are available to build a CI/CD pipeline in order to harden an application using NuoDB on Kubernetes. Before we dive into NuoDB’s chaos engineering, let’s give a quick introduction to NuoDB.
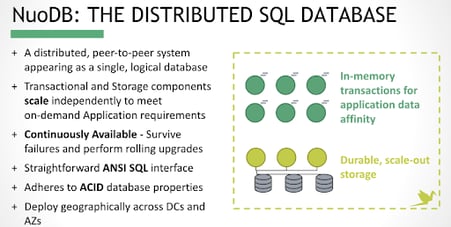
NuoDB is an elastic SQL database designed with distributed application deployment challenges in mind. It’s a SQL service that provides all the properties of ACID-compliant transactions and standard relational SQL language support. It’s also designed from the start as a distributed system that scales the way a cloud service has to scale, providing high availability and resiliency with no single points of failure. Different from traditional shared-disk or shared- nothing architectures, NuoDB’s presents a new kind of peer-to-peer, on-demand independence that yields high availability, low-latency, and a deployment model that is easy to manage.
Full stack view of a cloud native application using NuoDB and Kubernetes
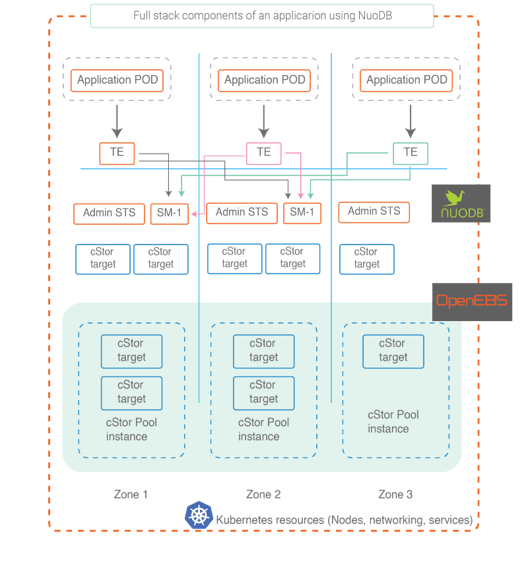
Developers and DevOps admins should really concentrate on building the test cases for the business logic involved in the application PODs. Pipelines for hardening the rest of the components of the stack, such as NuoDB implementation, OpenEBS implementation, and Kubernetes/OpenShift implementation, can be built using Litmus books. Later in this post, you will find reference implementation and example litmus books that you can use.
Elements of a NuoDB CI/CD pipeline
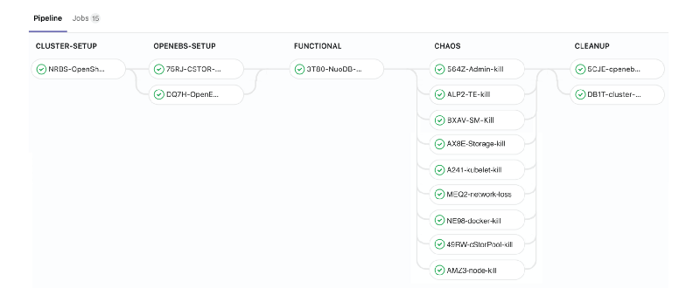 GitLab CI pipeline for NuoDB on OpenShift using OpenEBS as persistent storage
GitLab CI pipeline for NuoDB on OpenShift using OpenEBS as persistent storageThe figure above is a sample GitLab pipeline that is running OpenShift EE 3.11 and NuoDB 3.3 EE with Litmus. The stages are:
- CLUSTER-Setup
- OpenEBS-Setup
- FUNCTIONAL
- CHAOS
- CLEANUP
Litmus provides almost-ready books for every stage except FUNCTIONAL. Here, the Developers and DevOps admins should be spending time creating the tests for their applications. The remaining stages are generic enough that Litmus can accomplish the work for you with the tuning of the parameters.
A reference implementation of a NuoDB pipeline:
The NuoDB GitLab pipeline implementation for OpenShift EE platform and the corresponding Litmus books are all available in the OpenEBS GitHub repository at the following location.
openebs/e2e-openshiftAutomation of OpenEBS E2E testing on OpenShift On-Premise — openebs/e2e-openshiftgithub.com
NuoDB Solution Guide:
Here is a handy solution doc for implementing NuoDB using OpenEBS as persistent storage on OpenShift EE platform.

Solution guide : NuoDB on OpenShift with OpenEBS as persistent storage
If you are an ansible enthusiast or NuoDB user and wish to contribute to Litmus, feel free to join our community slack channel: slack.openebs.io and visit #litmus channel. We welcome any contributions and feedback!
Summary:
Building CI/CD pipelines for applications built on NuoDB, OpenEBS and Kubernetes/OpenShift is quick and easy and most of the pipeline is readily available through Litmus. You can use the readily available Litmus books to build Chaos Engineering into your GitLab pipelines.
LITMUS — Make Chaos Engineering simple for Kubernetes
Authors:
Uma Mukkara, COO @ MayaData (Uma Mukkara)
Sudarshan Darga, Lead Engineer — Chaos Engineering @ MayaData (Sudarshan Darga)
Example litmus jobs for OpenShift EE
Litmus book for OpenShift EE Cluster Setup
Litmus job for creating OpenShift Enterprise 3.10 cluster on on-premise virtual machines.
---
- hosts: localhost
vars_files:
- vars.yml
tasks:
- block:
- name: Getting master ip
shell: cat ip.csv | awk 'NR == 1'
register: master_ip
- name: Generating master SSH key
shell: ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no root@ 'ssh-keygen -t rsa -N \"\" -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa -y'
register: master_key
- name: Getting compute-nodes ip
shell: cat ip.csv | grep -v
register: compute_ip
- name: Generating compute-node SSH key
shell: ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no root@{{item}} 'ssh-keygen -t rsa -N \"\" -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa -y'
with_items: ""
- name: Copying ssh-key into master
shell: |
ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no root@ 'echo >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys'
eval 'ssh-agent'
- name: Copying the SSH key into compute nodes
shell: |
ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no root@{{item}} 'echo >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys'
eval 'ssh-agent'
with_items: ""
- name: SSH from master to each Nodes
shell: ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no root@ 'ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no root@{{item}} ls'
with_lines: cat ./ip.csv
- name: Generating random number
shell: date +%s
register: rand_num
- name: Setting up the master hostname
shell: |
ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no root@ 'echo master-. > /etc/hostname'
ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no root@ 'systemctl start systemd-hostnamed'
- name: Setting up the compute nodes hostname
shell: |
ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no root@ 'echo node-. > /etc/hostname'
ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no root@ 'systemctl start systemd-hostnamed'
with_together:
- [ '1', '2', '3' ]
- ""
#The VMs are already subscribed with some credentials. Need to unsubscribe the VMs & subscribe it again with new credentials.
- name: Unsubscribing the nodes
shell: ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no root@{{item}} 'subscription-manager unregister'
ignore_errors: true
with_lines: cat ./ip.csv
- name: Subscribing the nodes
shell: |
ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no root@{{item}} 'subscription-manager register --username= --password='
ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no root@{{item}} 'subscription-manager attach --auto'
ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no root@{{item}} 'subscription-manager refresh'
with_lines: cat ./ip.csv
- name: Getting the pool-id
shell: ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no root@ 'subscription-manager list --available --matches '*OpenShift*' | grep "Pool ID" | awk '\''NR == 1'\'' | awk '\''{print $3}'\'''
register: pool_id
- name: Attaching pool to each nodes
shell: |
ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no root@{{item}} 'subscription-manager attach --pool='
ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no root@{{item}} 'subscription-manager repos --enable="rhel-7-server-rpms" --enable="rhel-7-server-extras-rpms" --enable="rhel-7-server-ose-3.10-rpms" --enable="rhel-7-server-ansible-2.4-rpms"'
with_lines: cat ./ip.csv
- name: Joining the nodes to the DNS Server
shell: ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no root@{{item}} 'echo | realm join --user=Administrator '
with_lines: cat ./ip.csv
- name: SSH from master to master using DNS
shell: ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no root@ 'ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no root@master-. ls'
- name: SSH from master to compute nodes using DNS
shell: ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no root@ 'ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no root@node{{item}}-. ls'
with_items:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- name: Replacing master ip in inventory
replace:
path: ./inventory.yml
regexp: "master_ip"
replace: ""
- name: Replace compute node ip in inventory
replace:
path: ./inventory.yml
regexp: ""
replace: ""
with_together:
- [ 'node1_ip', 'node2_ip', 'node3_ip' ]
- ""
- name: Replacing master DNS in inventory
replace:
path: ./inventory.yml
regexp: "master_dns"
replace: "master-."
- name: Replacing nodes DNS in inventory
replace:
path: ./inventory.yml
regexp: ""
replace: ""
with_together:
- [ 'node1_dns', 'node2_dns', 'node3_dns' ]
- [ 'node1-.', 'node2-.', 'node3-.' ]
- name: Copying inventory into master
shell: scp -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no inventory.yml root@:/root/openshift-ansible/inventory/
- name: Checking out to release branch-3.10
shell: ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no root@ 'cd /root/openshift-ansible && git checkout release-3.10'
- name: Running Openshift pre-requisites
shell: ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no root@ 'ansible-playbook -i /root/openshift-ansible/inventory/inventory.yml /root/openshift-ansible/playbooks/prerequisites.yml -vv'
- name: Deploying openshift cluster
shell: ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no root@ 'ansible-playbook -i /root/openshift-ansible/inventory/inventory.yml /root/openshift-ansible/playbooks/deploy_cluster.yml -vv'
- name: Disabling selinux on each nodes
shell: ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no root@{{item}} 'setenforce 0'
with_lines: cat ./ip.csv
- name: Copying bash file in master & Executing
shell: |
scp -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no post_install_setting.sh root@:/root/
ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no root@ 'bash post_install_setting.sh && rm post_install_setting.sh'App deployers
Litmus job for deploying NuoDB EE using OpenEBS volumes for database requirements.
Prerequisites for running this litmus job is to have NuoDB Enterprise edition subscription and have docker images available in the cluster.
---
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
generateName: litmus-nuodb-
namespace: litmus
spec:
template:
metadata:
name: litmus
labels:
app: nuodb-deployment
spec:
serviceAccountName: litmus
restartPolicy: Never
containers:
- name: ansibletest
image: openebs/ansible-runner:ci
imagePullPolicy: Always
env:
- name: ANSIBLE_STDOUT_CALLBACK
#value: log_plays, actionable, default
value: default
- name: PROVIDER_STORAGE_CLASS
# Supported values: openebs-standard, local-storage, openebs-standalone
value: openebs-cstor-sparse
- name: NUODB_VERSION
value: ee
- name: APP_PVC
value: demo-vol-claim
- name: APP_NAMESPACE
value: nuodbns
# Application label
- name: APP_LABEL
value: 'app=nuodb'
# Use 'deprovision' for app-clean up
- name: ACTION
value: provision
# Set THP to disable in case platform is AWS or OpenShift
- name: THP
value: disable
command: ["/bin/bash"]
args: ["-c", "ansible-playbook ./nuodb/deployers/OpenShift/test.yml -i /etc/ansible/hosts -v; exit 0"]
Chaos jobs — NuoDB
Litmus job for inducing chaos on NuoDB application components such as Admin, Storage Manager and Transaction Engine.
For inducing various components chaos, user has to pass application component specific label as the Job Env to the litmus book.
---
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
generateName: nuodb-app-chaos-
namespace: litmus
spec:
template:
metadata:
labels:
name: nuodb-app-chaos
spec:
serviceAccountName: litmus
restartPolicy: Never
containers:
- name: ansibletest
image: openebs/ansible-runner:ci
env:
- name: ANSIBLE_STDOUT_CALLBACK
value: default
- name: APP_NAMESPACE
value: nuodbns
- name: APP_LABEL
value: 'nodetype=sm'
- name: DEPLOY_TYPE
value: statefulset
command: ["/bin/bash"]
args: ["-c", "ansible-playbook ./nuodb/chaos/app_pod_failure/test.yml -i /etc/ansible/hosts -vv; exit 0"]Chaos jobs — Networking
Litmus job for inducing network delays between application and openebs target pod.
---
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
generateName: nuodb-app-chaos-
namespace: litmus
spec:
template:
metadata:
labels:
name: nuodb-app-chaos
spec:
serviceAccountName: litmus
restartPolicy: Never
containers:
- name: ansibletest
image: openebs/ansible-runner:ci
env:
- name: ANSIBLE_STDOUT_CALLBACK
value: default
- name: APP_NAMESPACE
value: nuodbns
- name: APP_LABEL
value: 'nodetype=sm'
- name: DEPLOY_TYPE
value: statefulset
command: ["/bin/bash"]
args: ["-c", "ansible-playbook ./nuodb/chaos/app_pod_failure/test.yml -i /etc/ansible/hosts -vv; exit 0"]Chaos jobs — Storage
Litmus job for inducing OpenEBS cStor storage target kill and verify the application availability.
---
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
generateName: openebs-target-failure-
namespace: litmus
spec:
template:
metadata:
labels:
name: openebs-target-failure
spec:
serviceAccountName: litmus
restartPolicy: Never
containers:
- name: ansibletest
image: openebs/ansible-runner:ci
env:
- name: ANSIBLE_STDOUT_CALLBACK
#value: log_plays
#value: actionable
value: default
- name: APP_NAMESPACE
value: nuodbns
- name: TARGET_NAMESPACE
value: openebs
- name: APP_LABEL
value: 'nodetype=sm'
- name: APP_PVC
value: archive-sm-0
- name: LIVENESS_APP_LABEL
value: ""
- name: LIVENESS_APP_NAMESPACE
value: ""
- name: DATA_PERSISTENCY
value: ""
# CHOS_TYPE values : target-zrepl-kill , target-kill , target-delete
- name: CHAOS_TYPE
value: "target-zrepl-kill"
# TARGET_CONTAINER values: cstor-volume-mgmt , cstor-istgt
- name: TARGET_CONTAINER
value: "cstor-volume-mgmt"
command: ["/bin/bash"]
args: ["-c", "ansible-playbook ./percona/chaos/openebs_target_failure/test.yml -i /etc/ansible/hosts -vv; exit 0"]Litmus job for inducing OpenEBS cStor storage pool kill and verify the application availability.
---
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
generateName: openebs-pool-failure-
namespace: litmus
spec:
template:
metadata:
labels:
name: openebs-pool-failure
spec:
serviceAccountName: litmus
restartPolicy: Never
containers:
- name: ansibletest
image: openebs/ansible-runner:ci
imagePullPolicy: Always
env:
- name: ANSIBLE_STDOUT_CALLBACK
#value: log_plays
#value: actionable
value: default
- name: APP_NAMESPACE
value: nuodbns
- name: APP_LABEL
value: 'nodetype=sm'
- name: APP_PVC
value: archive-sm-0
- name: LIVENESS_APP_LABEL
value: ""
- name: LIVENESS_APP_NAMESPACE
value: ""
- name: DATA_PERSISTENCY
value: ""
- name: CHAOS_TYPE
value: "pool-kill"
- name: CHAOS_ITERATIONS
value: "2"
command: ["/bin/bash"]
args: ["-c", "ansible-playbook ./percona/chaos/openebs_pool_failure/test.yml -i /etc/ansible/hosts -vv; exit 0"]Chaos jobs — Kubernetes
Litmus job for inducing kubelet/docker service crash and verify impact on the application running on the node.
Note: This litmus job is specific to AWS platform.
---
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
generateName: openebs-app-svc-chaos-
namespace: litmus
spec:
template:
metadata:
labels:
name: openebs-app-svc-chaos
spec:
serviceAccountName: litmus
restartPolicy: Never
#nodeSelector:
# kubernetes.io/hostname:
containers:
- name: ansibletest
image: openebs/ansible-runner:ci
imagePullPolicy: Always
env:
- name: ANSIBLE_STDOUT_CALLBACK
#value: log_plays
#value: actionable
value: default
- name: OPERATOR_NAMESPACE
value: openebs
- name: APP_NAMESPACE
value: nuodbns
- name: APP_LABEL
value: 'nodetype=sm'
- name: APP_PVC
value: archive-sm-0
# Set value to kubelet/docker
- name: SVC_CHAOS
value: docker
- name: CHAOS_DURATION
value: "300" # in seconds
- name: LIVENESS_APP_LABEL
value: ""
- name: LIVENESS_APP_NAMESPACE
value: ""
- name: PLATFORM
value: "AWS"
command: ["/bin/bash"]
args: ["-c", "ansible-playbook ./percona/chaos/openebs_app_svc_chaos/test.yml -i /etc/ansible/hosts -vv; exit 0"]
This article was first published on Apr 15, 2019 on OpenEBS's Medium Account






Game changer in Container and Storage Paradigm- MayaData gets acquired by DataCore Software
Don Williams
Don Williams
Managing Ephemeral Storage on Kubernetes with OpenEBS
Kiran Mova
Kiran Mova
Understanding Persistent Volumes and PVCs in Kubernetes & OpenEBS
Murat Karslioglu
Murat Karslioglu