An enhanced schema for OpenEBS cStor Pool Management
CStor Data Engine is popular for workloads needing efficient capacity management, replicas, point in time snapshots, incremental backups, etc. Since achieving Beta last year, cStor Data Engine has been powering many Stateful Applications, including a variety of databases.
While users love cStor for its data management capabilities, they have been providing feedback that it is not as easy to use as Jiva. We have started working on user feedback starting with OpenEBS 1.2 release and incrementally enhancing the cStor functionality.
As cStor is already running in production, the new changes are being introduced via a set of new cStor Custom Resources, which will get into in a bit. The users can continue to use the current schema, as we stabilize the new design and support a seamless migration. You can help us improve by providing feedback on the new design here or by raising issues.
To give a high-level overview of the new design, the following will be changed:
- A new component/deployment called cspc-operator will be deployed for managing the new custom resources.
- CSPC — cStor Pool Cluster will be replacing the SPC. The spec of the CSPC has been modified to provide cleaner abstractions for managing blockdevices on each node.
- CSPI — cStor Pool Instance will be replacing CSP.
The new schema will only support manual cStor Pools creation as we learned that supporting both manual and auto using a single customer CR can lead to more confusion. In future releases, a new schema will be introduced to support the automatic creation of the cStor Pools.
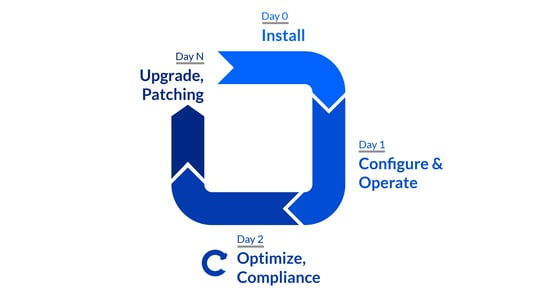
CSPC can be used to provision cStor pool as well as carry out day 2 pool operations such as: Following storage day 2 operations are supported via the CSPC schema:
- Pool Expansion ( Supported in OpenEBS version >=1.2, alpha )
- Pool Deletion ( Supported in OpenEBS version >=1.2, alpha )
- Pool Scale Up ( Supported in OpenEBS version >=1.2, alpha )
- Block Device Replacement ( Supported in OpenEBS version >=1.5, alpha)
Let us go through a short hands-on tutorial to understand these.
The tutorial will provision striped cStor pools and perform operations on them (this can be done for other cStor raid groups too and I will post that in a separate blog).
Prerequisites
- Kubernetes cluster of version >= 1.14 with 3 worker nodes.
- Attach at least 2 disks to each of the nodes to follow up with the tutorial. I am using GKE and steps to create and attach a disk to a node are given in the following link :
https://cloud.google.com/sdk/gcloud/reference/compute/disks/create
https://cloud.google.com/sdk/gcloud/reference/compute/instances/attach-disk
If you are using other providers, check with their reference manuals on how to attach a disk. Also, feel free to reach out on the OpenEBS slack channel if you need any assistance. - I have used the following script to create 6 disks.
{ for i in {1..6}; do gcloud compute disks create demo-disk-$i — zone=us-central1-a — size=100GB; done; } - Now, I will attach 2 disks to each of the nodes. I have used the following commands to attach.
for i in {1..2}; do gcloud compute instances attach-disk gke-cstor-demo-default-pool-3385ab41–2ldq — disk demo-disk-$i — device-name demo-disk-$i — zone us-central1-a; done
for i in {3..4}; do gcloud compute instances attach-disk gke-cstor-demo-default-pool-3385ab41-bb69 — disk demo-disk-$i — device-name demo-disk-$i — zone us-central1-a; done
for i in {5..6}; do gcloud compute instances attach-disk gke-cstor-demo-default-pool-3385ab41-hrmr — disk demo-disk-$i — device-name demo-disk-$i — zone us-central1-a; done
- Install OpenEBS 1.5. Run following to install: ( Note that block device replacement support starts from OpenEBS version 1.5. There will be a separate blog post to describe that.)
kubectl apply -f
https://openebs.github.io/charts/openebs-operator-1.5.0.yaml- Install CStor-Operator. Run following to install:
$ kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openebs/openebs/master/k8s/cstor-operator.yamlPool Provisioning
You need to specify cStor pool intent in a CSPC YAML to provision cStor pools on nodes. I am going to provision 3 stripe cStor pools. Let us prepare a CSPC YAML now.
Following command list all block devices which represent your attached disks. I am going to pick 1 block device from each node to form a CSPC YAML.
$ kubectl get bd -n openebs
NAME NODENAME SIZE CLAIMSTATE STATUS AGE
blockdevice-474d20376a541a8fb372d44f5bc361ea gke-cstor-demo-default-pool-3385ab41-hrmr 107374182400 Unclaimed Active 34s
blockdevice-9773ccb731e4e3e10c2838411f5f8b2a gke-cstor-demo-default-pool-3385ab41-bb69 107374182400 Unclaimed Active 37s
blockdevice-9c8df120e17379bfd1fe5c3ce9aa8185 gke-cstor-demo-default-pool-3385ab41-bb69 107374182400 Unclaimed Active 37s
blockdevice-ada8ef910929513c1ad650c08fbe3f36 gke-cstor-demo-default-pool-3385ab41-2ldq 107374182400 Unclaimed Active 34s
blockdevice-d2d59218ed78560b206143ab0641470c gke-cstor-demo-default-pool-3385ab41-hrmr 107374182400 Unclaimed Active 34s
blockdevice-f6408e135943e1ee45171034655a8b88 gke-cstor-demo-default-pool-3385ab41-2ldq 107374182400 Unclaimed Active 34s
My CSPC YAML is on the following link (you can copy/download and make changes accordingly).
Save the above file with your changes and apply the above YAML to provision cStor pools.
$ kubectl apply -f
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openebs/elves/a8ce5d6401f1ab829a35214ea01c284ccfb03c13/demo/cspc/cspc-stripe.yaml
cstorpoolcluster.openebs.io/cspc-stripe created
$ kubectl get cspi -n openebs
NAME HOSTNAME ALLOCATED FREE CAPACITY STATUS AGE
cspc-stripe-8vtx gke-cstor-demo-default-pool-3385ab41-2ldq 69.5K 99.5G 99.5G ONLINE 99s
cspc-stripe-h7kl gke-cstor-demo-default-pool-3385ab41-bb69 69.5K 99.5G 99.5G ONLINE 99s
cspc-stripe-x9pw gke-cstor-demo-default-pool-3385ab41-hrmr 69.5K 99.5G 99.5G ONLINE 99s
If you want to deploy a workload to use the cStor pool, go through the following cStor CSI driver link:
https://github.com/openebs/cstor-csi/blob/master/README.md
In the next section, we will do pool expansion.
Pool Expansion
Let us expand one cStor stripe pool on a node by editing the CSPC cspc-stripe.
$ kubectl edit cspc cspc-stripe -n openebs
Simply, add one more block device as follows. Make sure you do not put a block device that is a part of any other CSPC. I have added block device blockdevice-d2d59218ed78560b206143ab0641470c in my case.
$ kubectl edit cspc cspc-stripe -n openebs
...
spec:
pools:
- nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/hostname: gke-cstor-demo-default-pool-3385ab41-hrmr
poolConfig:
cacheFile: ""
compression: "off"
defaultRaidGroupType: stripe
overProvisioning: false
raidGroups:
- blockDevices:
- blockDeviceName: blockdevice-474d20376a541a8fb372d44f5bc361ea
capacity: ""
devLink: ""
# Block device added. This must be attached to node
# gke-cstor-demo-default-pool-3385ab41-hrmr and should not be used by
# by any other CSPC.
- blockDeviceName: blockdevice-d2d59218ed78560b206143ab0641470c
isReadCache: false
isSpare: false
isWriteCache: false
type: stripe
...
Save the above changes.
$ kubectl get cspi -n openebs
NAME HOSTNAME ALLOCATED FREE CAPACITY STATUS AGE
cspc-stripe-8vtx gke-cstor-demo-default-pool-3385ab41-2ldq 268K 99.5G 99.5G ONLINE 17m
cspc-stripe-h7kl gke-cstor-demo-default-pool-3385ab41-bb69 292K 99.5G 99.5G ONLINE 17m
cspc-stripe-x9pw gke-cstor-demo-default-pool-3385ab41-hrmr 232K 199G 199G ONLINE 17m
You can see that the pool cspc-stripe-x9pw got expanded. (Re-run the get cspi command if the bigger size is not shown instantaneously). Similarly, you can expand the other stripe cStor pools of the CSPC.
Pool Deletion
To delete a cStor pool from node simple remove the node configuration from the CSPC.
Let us delete one pool from CSPC cspc-stripe.
$ kubectl edit cspc cspc-stripe -n openebs
I have removed following entire config from the CSPC to delete pool on host gke-cstor-demo-default-pool-3385ab41-2ldq.
...
- nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/hostname: gke-cstor-demo-default-pool-3385ab41-2ldq
poolConfig:
cacheFile: ""
compression: "off"
defaultRaidGroupType: stripe
overProvisioning: false
raidGroups:
- blockDevices:
- blockDeviceName: blockdevice-ada8ef910929513c1ad650c08fbe3f36
capacity: ""
devLink: ""
isReadCache: false
isSpare: false
isWriteCache: false
type: stripe
...
After you are done removing, save it and you will see that pool on that node has been deleted.
$ kubectl get cspi -n openebs
NAME HOSTNAME ALLOCATED FREE CAPACITY STATUS AGE
cspc-stripe-h7kl gke-cstor-demo-default-pool-3385ab41-bb69 335K 99.5G 99.5G ONLINE 25m
cspc-stripe-x9pw gke-cstor-demo-default-pool-3385ab41-hrmr 372K 199G 199G ONLINE 25m
You can see that only two stripe pools are present.
Pool Scale Up
We can even create a pool on other nodes by adding node config to the CSPC YAML. It is just the reverse of pool deletion.
Let's try to add the same node config that we removed to again create the pool on the node. Make sure that while copy, pasting and editing indentation of YAML is not disturbed else error will be thrown and YAML will not be persisted.
Add the removed config from the pool deletion section to the CSPC.
$ kubectl get cspi -n openebs
NAME HOSTNAME ALLOCATED FREE CAPACITY STATUS AGE
cspc-stripe-h7kl gke-cstor-demo-default-pool-3385ab41-bb69 318K 99.5G 99.5G ONLINE 30m
cspc-stripe-twvv gke-cstor-demo-default-pool-3385ab41-2ldq 50K 99.5G 99.5G ONLINE 9s
cspc-stripe-x9pw gke-cstor-demo-default-pool-3385ab41-hrmr 380K 199G 199G ONLINE 30m
You can see that a new pool cspc-stripe-twvv has come up online.
You can also delete the CStorPoolCluster too. If you do so, all the CStorPoolInstances associated with it will get deleted.
kubectl delete cspc <cspc-name> <cspc-namespace> NOTES:
- Whenever a block device is used for pool creation or expansion a blockdeviceclaim CR is created and the block device will show a Claimed status.
The following are the commands to visualize this.
kubectl get blockdevice -n openebs
kubectl get blockdeviceclaim -n openebs - Whenever a pool is deleted for a CSPC by removing the node config, the associated block-device is not ‘Unclaimed’ and if the same block device needs to be used in another CSPC, the associated blockdeviceclaim needs to be cleared manually. Although, the block-device can be again used for the same CSPC.
To unclaim a block device claim, below are the steps.
$ kubectl get bdc -n openebs
NAME BLOCKDEVICENAME PHASE AGE
bdc-cstor-83b8e958-d978-11e9-b0e6-42010a800189 blockdevice-9773ccb731e4e3e10c2838411f5f8b2a Bound 32m
bdc-cstor-8581dac0-d978-11e9-b0e6-42010a800189 blockdevice-ada8ef910929513c1ad650c08fbe3f36 Bound 32m
bdc-cstor-85bddd0e-d978-11e9-b0e6-42010a800189 blockdevice-474d20376a541a8fb372d44f5bc361ea Bound 32m
bdc-cstor-85c0fd2a-d978-11e9-b0e6-42010a800189 blockdevice-d2d59218ed78560b206143ab0641470c Bound 15m
Let us say, we want to unclaim block device blockdevice-d2d59218ed78560b206143ab0641470c, then we need to delete the associated blockdeviceclaim i.e. bdc-cstor-85c0fd2a-d978–11e9-b0e6–42010a800189.
$ kubectl edit bdc bdc-cstor-85c0fd2a-d978-11e9-b0e6-42010a800189 -n openebs
Remove the finalizer "cstorpoolcluster.openebs.io/finalizer" by editing the bdc from above command.
After that, execute following
$ kubectl delete bdc bdc-cstor-85c0fd2a-d978-11e9-b0e6-42010a800189 -n openebs
Now the device will get unclaimed. Please note the following:
BDC CRs should be deleted only when their association with CSPC has been removed. Otherwise, data corruption can happen.
Block Device Replacement
The CSPC operator in OpenEBS (≥1.5 version ) enables you to do the replacement of the block devices in case it has gone bad. I will follow up with another blog post that will cover this block device replacement scenario.
Hopefully this tutorial helps in understanding the pool operations steps.
If you have any questions or encounter any problems, feel free to reach out to me on the OpenEBS slack channel.







Game changer in Container and Storage Paradigm- MayaData gets acquired by DataCore Software
Don Williams
Don Williams
Managing Ephemeral Storage on Kubernetes with OpenEBS
Kiran Mova
Kiran Mova
Understanding Persistent Volumes and PVCs in Kubernetes & OpenEBS
Murat Karslioglu
Murat Karslioglu