The code that is never executed for users is like a digital waste product. To prevent the building of waste and to showcase the results of code on the Kubernetes environment, we can use CI Dashboard, with chaos testing.
The CI dashboard allows the users to view the commit and release based build along with chaos test using litmus on a different platform with different Kubernetes versions.
In this tutorial, we’ll go through all the steps for setting up the Ci Dashboard
- Create a project
- Push the code to GitHub
- Setup the CI of the project using gitlab
- Select the chaos test from litmus.
- Add the script in gitlab yaml to create pipelines for executing the chaos tests
- Build a CI dashboard(ex: openebs.ci ) to display the gitlab pipeline history and status
- Conclusion
Step 1: Create a project
Create a project and write some automated test for it, Also add the Dockerfile in the project to set up the CI.
Step 2: Put the codes on GitHub
Create a repository on GitHub and add .gitignore file for ignoring the auto-generated folder or file, Follow the below script to put changes to GitHub.
| $ git init $ git add . $ git commit -s -m "Initial commit" $ git remote add origin <origin_url>.git $ git push origin master |
Step 3: Setup the CI using gitlab
Add .gitlab.yaml file to project and write the build and test steps in it. (Ex: https://github.com/openebs/maya/blob/master/.gitlab-ci.yml). Import the project in gitlab from GitHub. Setup the gitlab pipeline environment variable to push the docker image or any other if required. Add the pipeline trigger command in .gitlab.yaml file.
Step 4: Selection of chaos test
Select the chaos test(litmus book) from litmus repository or write your own litmus book if needed which will test the product performance on different kubernetes version as well as different cloud vendors.
Step 5: Add script in gitlab.yaml
Create a repository for the execution of the platform-based pipeline. Add .gitlab.yaml file and related script to create a cluster or using the executing cluster and run the different chaos test in different stages of the pipeline.
Reference of .gitlab.yaml file
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openebs/e2e-packet/master/.gitlab-ci.yml
| cleanup-packet: when: always image: chandankumar4/packet:v4 dependencies: - packet-cluster stage: CLUSTER-CLEANUP script: - chmod 755 ./script/packet-cleanup - ./script/packet-cleanup |
Step 6: Build a CI dashboard
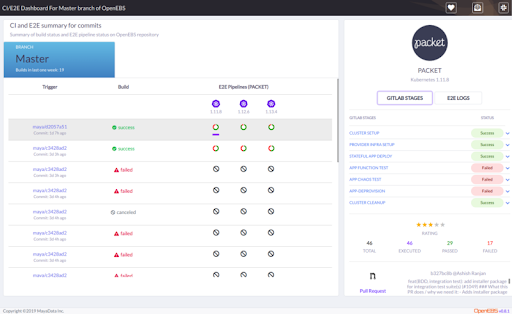
Create a project called Ci dashboard backend which will fetch the pipeline details form gitlab, By accessing their API and expose the same on different API after some enhancement. Create another project called Ci dashboardwhich will display the gitlab pipeline details by accessing the data from backend API.
Step 7: Conclusion
CI dashboard will display the build history of the imported project and their performance on a different platform with different Kubernetes version.
References
openebs/ci-e2e-dashboardContribute to openebs/ci-e2e-dashboard development by creating an account on GitHub.github.com
openebs/ci-e2e-dashboard-go-backendOpenEBS CI Dashboard backend using Go and PostgreSQL. — openebs/ci-e2e-dashboard-go-backendgithub.com
openebs/mayaOpenEBS Maya extends Kubernetes capabilities to orchestrate CAS containers. — openebs/mayagithub.com
This article was first published on Apr 26, 2019 on OpenEBS's Medium Account






Managing Ephemeral Storage on Kubernetes with OpenEBS
Kiran Mova
Kiran Mova
Why OpenEBS 3.0 for Kubernetes and Storage?
Kiran Mova
Kiran Mova
Deploy PostgreSQL On Kubernetes Using OpenEBS LocalPV
Murat Karslioglu
Murat Karslioglu